If you’re using Laragon to develop web applications and need to run Python scripts through Apache, you might encounter an issue where Python isn’t recognized in your environment. Don’t worry—fixing it is simple! Here’s a step-by-step guide to adding Python to Laragon’s Apache environment, explained in an easy and straightforward way.
Why Doesn’t Python Work?
When Apache tries to run Python, it looks for it in a specific list of folders (called the “PATH”). If Python’s folder isn’t on this list, Apache won’t recognize it. Our job is to show Apache where Python is located so it can use it properly.
Step 1: Find Your Python Path
First, we need to find where Python is installed:
- Open File Explorer.
- Look for a folder named something like:
C:\Python39(for Python 3.9)C:\Python311(for Python 3.11)
- Note down this folder path.
Step 2: Open Laragon’s Apache Configuration
Now, let’s update Laragon’s Apache configuration so it recognizes Python:
- Go to your Laragon folder (usually
D:\laragon\). - Open this folder:
D:\laragon\etc\apache2\. - Find a file named
fcgid.confand open it in a text editor (like Notepad++).
Step 3: Add Python to Apache’s Environment
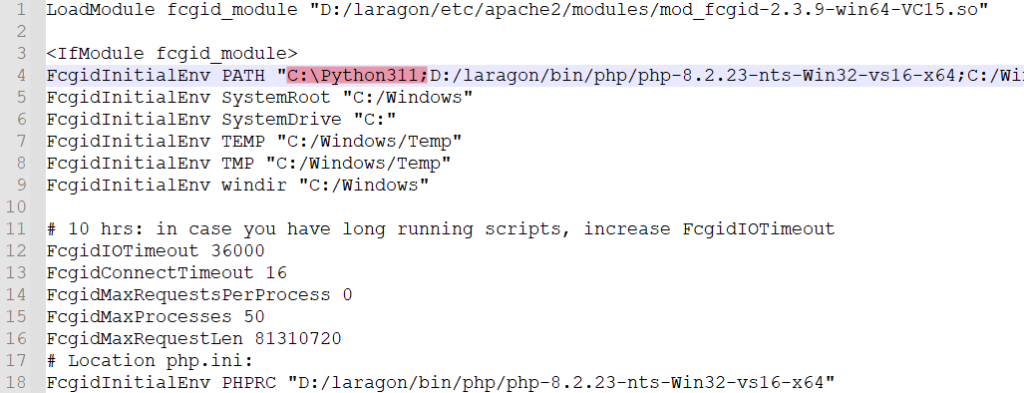
Inside the fcgid.conf file, find this line:
FcgidInitialEnv PATH
It should already contain some paths for PHP and system folders. Add your Python path to it. For example:
Before:
FcgidInitialEnv PATH "D:/laragon/bin/php/php-8.2.23-nts-Win32-vs16-x64;C:/Windows/system32;C:/Windows;C:/Windows/System32/Wbem;"
After:
FcgidInitialEnv PATH "C:\Python311;D:/laragon/bin/php/php-8.2.23-nts-Win32-vs16-x64;C:/Windows/system32;C:/Windows;C:/Windows/System32/Wbem;"
This tells Apache where to find Python.
Step 4: Save and Restart Apache
- Save the
fcgid.conffile. - Restart Apache by opening Laragon and clicking Menu > Apache > Restart.
Step 5: Test It Out
To check if Apache recognizes Python, create a PHP file in your web root folder (usually D:/laragon/www/). Name it test.py.php and add this code:
<?php
$output = [];
exec('python --version', $output);
echo implode("\n", $output);
?>
Open this file in your browser, e.g., http://localhost/test.py.php. If everything is set up correctly, you’ll see the Python version displayed.
Conclusion
Congratulations! You’ve successfully added Python to Laragon’s Apache environment. Now you can run Python scripts directly through Apache. If this guide helped you, share it with your fellow programmers—it might save them a lot of time!